
Quick Start
This C++ library provides functions to save/load/serialize/deserialize data easily. Adding type can be done be defining only one function per extra type you wan to use !
#include "phoenix_data_stream.h"
...
//Save data to file
std::vector<int> vecData;
data_save("someFile.data", vecData);
//Load data from file
std::vector<int> vecDataLoaded;
data_load("someFile.data", vecDataLoaded);
//Get size of data in bytes
size_t dataSize(data_size(vecDataLoaded);
//Serialise data in stream
int data(42);
DataStreamMsg message(data_size(data));
DataStreamIter iter = message.data();
data_message_save(iter, data);
DataStreamMsg message(data_size(data));
DataStreamIter iterRead = message.data();
int loadedValue(0);
data_message_load(iterRead, loadedValue);
And if you want to add your own type :
#include "phoenix_data_stream.h"
struct Shadok{
///Age the Shadok
int p_age;
///Name of the Shadok
std::string name;
};
///@brief Generic Shadok serialisation/deserialisation function
template<typename Stream, DataStreamMode::DataStreamMode Mode>
struct DataStream<Stream, Mode, Shadok>{
//You can declare only the attribute you want
static bool data_stream(Stream & ds, Shadok & data){
bool b = DataStream<Stream, Mode, int>::data_stream(ds, data.age);
b &= DataStream<Stream, Mode, std::string>::data_stream(ds, data.name);
return b;
}
};
If you specialised once the function above, you can now use the Shadok with all the previous functions :
- data_save : to save binary files that contain Shadok, std::vector, std::list or std::map of Shadok
- data_load : to load binary files
- data_size : to get the size in bytes of the given data
- data_message_save : to serialise data in a message
- data_message_load : to deserialise data from a message
You can see unit tests for more examples.
Expanding to enumerate
In the case of enumerate types, we have to pass through an int to save or load it.
The simple way consists to use the PHOENIX_DATA_STREAM_ENUM to declare enum's interface the proper way :
#include "phoenix_data_stream.h"
namespace ShadokType{
///Type of the Shadok we want to serialized
enum ShadokType{
NONE = 0, //Nothing to do
HAUT = 1, //Shadok from the top of the planet
BAS = 2 //Shadok from the bottom of the planet
};
}
PHOENIX_DATA_STREAM_ENUM(ShadokType::ShadokType)
Here is a full example to integrate an enumerate type in the Data Stream workflow and to show what is under the above macro :
#include "phoenix_data_stream.h"
namespace ShadokType{
///Type of the Shadok we want to serialized
enum ShadokType{
NONE = 0, //Nothing to do
HAUT = 1, //Shadok from the top of the planet
BAS = 2 //Shadok from the bottom of the planet
};
}
///@brief Generic ShadokType deserialisation, load and size function for a ShadokType::ShadokType
template<typename Stream>
struct DataStream<Stream, DataStreamMode::READ, ShadokType::ShadokType>{
///Generic function to load/deserialise ShadokType
// @param[out] ds : Stream to be used
// @param data : ShadokType to be loaded
// @return true on success, false otherwise
static bool data_stream(Stream & ds, ShadokType::ShadokType & data){
int value(0);
bool b = DataStream<Stream, DataStreamMode::READ, int>::data_stream(ds, value);
data = (ShadokType::ShadokType)value;
return b;
}
};
///@brief Generic ShadokType serialisation, save and size function for a ShadokType::ShadokType
template<typename Stream>
struct DataStream<Stream, DataStreamMode::WRITE, ShadokType::ShadokType>{
///Generic function to save/serialise ShadokType
// @param[out] ds : Stream to be used
// @param data : ShadokType to be saved
// @return true on success, false otherwise
static bool data_stream(Stream & ds, ShadokType::ShadokType & data){
int value = (int)data;
return DataStream<Stream, DataStreamMode::WRITE, int>::data_stream(ds, value);
}
};
Code generator
You can also a PhoenixFileGenerator code generator to save time when you define data you want to exchange with classes.
Our previous example can be defined with a simple configuration in the file Shadok.pdata :
///@brief Test Shadok
Shadok {
///Age of the Shadok
int age;
///Name of the Shadok
std::string name;
}
Then, you can call :
phoenix_filegenerator class -c Shadok.pdata --datastream
To generate the corresponding Shadok class with the PhoenixDataStream interface.
Data format
The data format of PhoenixDataStream is very simple. Types are described as they are :
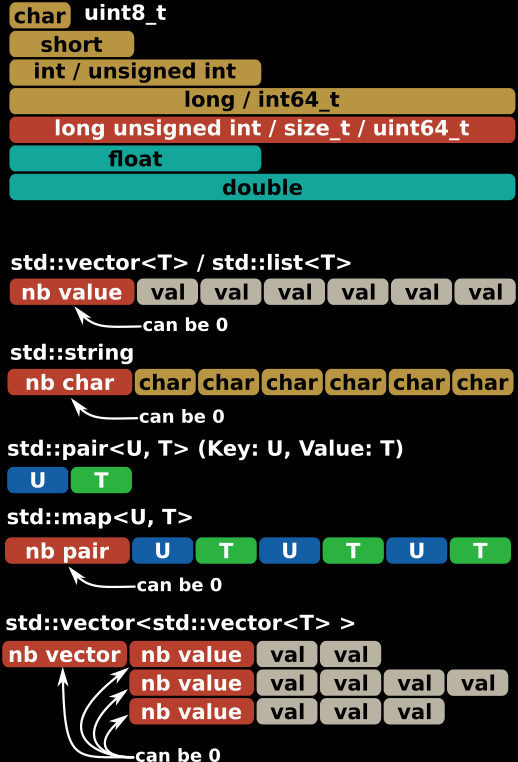
Warning : - There is no definition in PhoenixDataStream to handle PString and PPath - Endianess is not handled by PhoenixDataStream but by PhoenixEndianess
Code
Source code is available here
Documentation
User documentation can be found here
Requirements
- c++ compiler (tested with g++ 11,12,13 and clang >= 14)
- PhoenixCMake
- cmake > 3
- make
Installation for Users
Install packages using pixi conda manager
Each Phoenix package is packaged using pixi, a modern and fast conda package manager. Pixi simplifies environment management and installation, ensuring reproducible builds and easy dependency handling. Phoenix packages are hosted on prefix.dev, with two dedicated channels: - phoenix for stable releases. - phoenix-dev for development packages. These packages are build from the latest developments in the Phoenix projects, they can be deleted at any moment. Using pixi is recommended for people that get started using or developing Phoenix packages. It will speed up your setup, handle the dependencies resolution and updates, and allow you to use the tasks defined for common development operations (run test, build doc, etc.)
To install the package in a globally accessible location and exposes its command line applications:
pixi global install -c conda-forge -c https://prefix.dev/phoenix phoenixdatastream
Using this command you can specify :
- the channel where the package is located: https://prefix.dev/phoenix
- the version you want to install, for instance "phoenixdatastream==0.8.0"
To use this library as a dependency in your own pixi projects, you must add the dependency into your workspace. First, add the Phoenix channel into your workspace:
[workspace]
channels = [
"https://prefix.dev/phoenix"
]
then add the dependency on the library. For instance to add the library in your default environment:
pixi add phoenixdatastream
Install from sources using pixi
To develop the library using a pixi installation, download the sources and then you will be able to run tasks define in the pixi.toml file using pixi:
git clone https://gitlab.in2p3.fr/CTA-LAPP/PHOENIX_LIBS2/PhoenixDataStream.git
cd PhoenixDataStream
pixi install -a
pixi run test # task defined in the pixi.toml used to run the tests
The basic available tasks in the pixi.toml are :
| | Objective | Inputs | Outputs |
|-----------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------------------:|:-------------------:|
| pixi run test | Run the tests of the current package | - | - |
| pixi run coverage | Generate the coverage report of the current project. | Output folder for coverage reports. Default is coverage | coverage folder |
| pixi run doc | Generate documentation of the current project | docDir Output folder for documentation | docDir folder |
Install from sources
git clone https://gitlab.in2p3.fr/CTA-LAPP/PHOENIX_LIBS2/serialize-io/PhoenixDataStream.git
cd PhoenixDataStream
./install.sh
Then PhoenixDataStream is installed in your $HOME/usr.
If you prefer a customized install path you can do :
git clone https://gitlab.in2p3.fr/CTA-LAPP/PHOENIX_LIBS2/serialize-io/PhoenixDataStream.git
cd PhoenixDataStream
./install.sh /your/install/path
If you prefer a customized install path with custom compilation you can do :
git clone https://gitlab.in2p3.fr/CTA-LAPP/PHOENIX_LIBS2/serialize-io/PhoenixDataStream.git
cd PhoenixDataStream
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake .. $(phoenixcmake-config --cmake)
make -j `nproc`
make install -j `nproc`
The nproc gives the number of cores of the computer. If you want a build on one core you can just type :
make
make install
Update PhoenixDataStream
If you want to update the software :
git clone https://gitlab.in2p3.fr/CTA-LAPP/PHOENIX_LIBS2/serialize-io/PhoenixDataStream.git
cd PhoenixDataStream
./update.sh
If you want to update the software with a custom install path :
git clone https://gitlab.in2p3.fr/CTA-LAPP/PHOENIX_LIBS2/serialize-io/PhoenixDataStream.git
cd PhoenixDataStream
./update.sh /your/install/path